Algorithm
Kadanes Algorithm (Longest sum contiguous subarray)
for each elements in array:
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + array[i]
if max_ending_here < array[i]:
max_ending_here = array[i]
if max_value < max_ending_here:
max_value = max_ending_here
Topological Sorting Algorithm (geeksforgeeks)
def topologicalSortUtil(self,v,visited,stack):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[v]:
if visited[i] == False:
self.topologicalSortUtil(i,visited,stack)
# Push current vertex to stack which stores result
stack.insert(0,v)
Kahn’s Algorithm (geeksforgeeks)
def topologicalSort(self):
# Create a vector to store indegrees of all
# vertices. Initialize all indegrees as 0.
in_degree = [0]*(self.V)
# Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees of
# vertices. This step takes O(V + E) time
for i in self.graph:
for j in self.graph[i]:
in_degree[j] += 1
# Create an queue and enqueue all vertices with
# indegree 0
queue = []
for i in range(self.V):
if in_degree[i] == 0:
queue.append(i)
# Initialize count of visited vertices
cnt = 0
# Create a vector to store result (A topological
# ordering of the vertices)
top_order = []
# One by one dequeue vertices from queue and enqueue
# adjacents if indegree of adjacent becomes 0
while queue:
# Extract front of queue (or perform dequeue)
# and add it to topological order
u = queue.pop(0)
top_order.append(u)
# Iterate through all neighbouring nodes
# of dequeued node u and decrease their in-degree
# by 1
for i in self.graph[u]:
in_degree[i] -= 1
# If in-degree becomes zero, add it to queue
if in_degree[i] == 0:
queue.append(i)
cnt += 1
Convert a binary tree to a graph
def dfs(node, parent,graph):
if not node:
return
if parent:
graph[node].append(parent)
if node.right:
graph[node].append(node.right)
dfs(node.right, node, graph)
if node.left:
graph[node].append(node.left)
dfs(node.left, node, graph)
dfs(root,None,graph)
Sieve of Eratosthenes
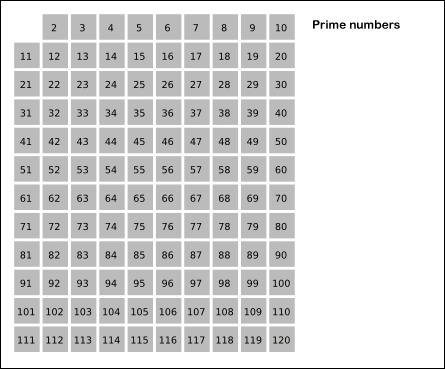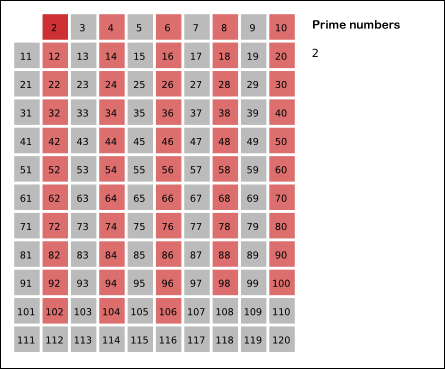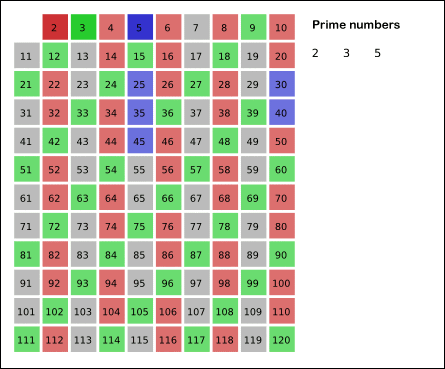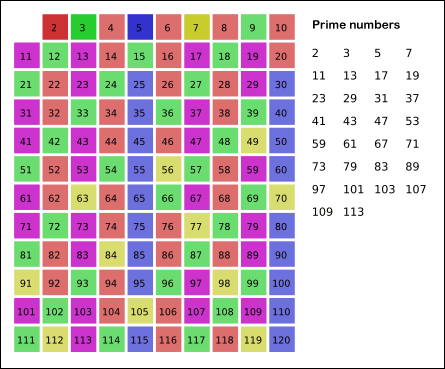
(from wikipedia)
n = number # range of the number
a = [False,False] + [True]*(n-1)
primes = []
for i in range(2,n+1):
if a[i]:
primes.append(i)
for j in range(2*i, n+1, i):
a[j] = False
print(primes)
Boyer-Moore vote Algorithm
(https://gregable.com/2013/10/majority-vote-algorithm-find-majority.html)
candidate = 0
count = 0
for value in input:
if count == 0:
candidate = value
if candidate == value:
count += 1
else:
count -= 1
De Bruijn sequence Algorithm
De Brujin sequences, contating combinations of length n using k digits, have length k^n.
Number of De Brujin sequences is equal to number of Euler cycles, which is K!^K^n-1 / K^n.
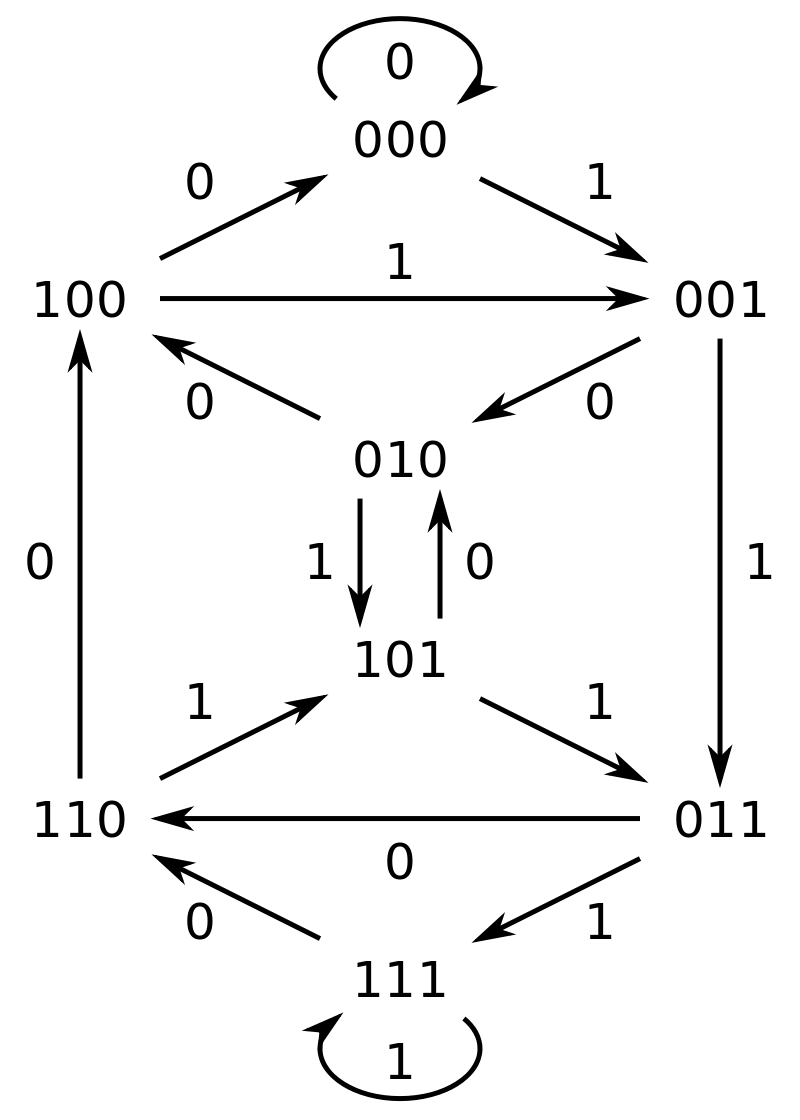
def de_bruijn(k, n: int) -> str:
"""de Bruijn sequence for alphabet k
and subsequences of length n.
"""
try:
# let's see if k can be cast to an integer;
# if so, make our alphabet a list
_ = int(k)
alphabet = list(map(str, range(k)))
except (ValueError, TypeError):
alphabet = k
k = len(k)
a = [0] * k * n
sequence = []
def db(t, p):
if t > n:
if n % p == 0:
sequence.extend(a[1 : p + 1])
else:
a[t] = a[t - p]
db(t + 1, p)
for j in range(a[t - p] + 1, k):
a[t] = j
db(t + 1, t)
db(1, 1)
return "".join(alphabet[i] for i in sequence)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De_Bruijn_sequence
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iPLQgXUiU14&vl=en-GB
Prims Algorithm
Prim’s (also known as Jarník’s) algorithm is a greedy algorithm that finds a minimum spanning tree for a weighted undirected graph. (wikipedia)
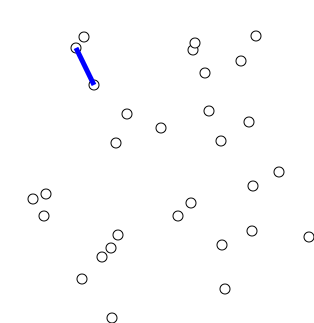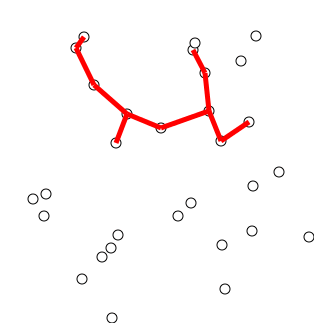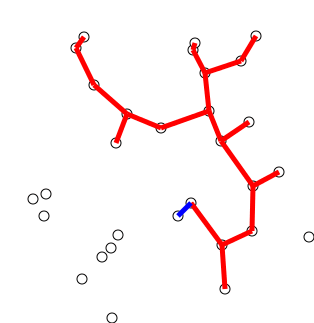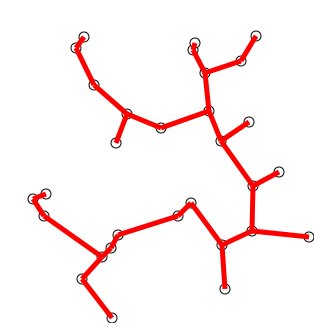
def prims(graph):
value = [float('inf')] * n
setMst = [False] * n
parent = [0] * n
value[0] = 0
parent[0] = -1
for i in range(n-1):
u = select_min(setMst,value)
setMst[u] = True
for j in range(n):
if graph[u][j] != 0 and setMst[j] == False and value[j] > graph[u][j]:
value[j] = graph[u][j]
parent[j] = u
Kruskals Algorithm
Dijkstra Algorithm
Dijkstra’s algorithm (or Dijkstra’s Shortest Path First algorithm, SPF algorithm) is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph, which may represent, for example, road networks. But it does not work with negative numbers (wikipedia)
while True:
for neighbour, distance in distances[current].items():
if neighbour not in unvisited: continue
newDistance = currentDistance + distance
if unvisited[neighbour] is None or unvisited[neighbour] > newDistance:
unvisited[neighbour] = newDistance
visited[current] = currentDistance
del unvisited[current]
if not unvisited: break
candidates = [node for node in unvisited.items() if node[1]]
current, currentDistance = sorted(candidates, key = lambda x: x[1])[0]
Bellman Ford Algorithm
The Bellman–Ford algorithm is an algorithm that computes shortest paths from a single source vertex to all of the other vertices in a weighted digraph.[1] It is slower than Dijkstra’s algorithm for the same problem, but more versatile, as it is capable of handling graphs in which some of the edge weights are negative numbers. (wikipedia)
values = [0] + [float('inf')] * N
for _ in range(N-1):
cnt = 0
for u,v,w in edges:
if values[u] != float('inf') and values[u] + w < values[v]:
values[v] = values[u] + w
cnt += 1
if cnt == 0:
break
Floyd Warshall Algorithm
Floyd–Warshall algorithm is an algorithm for finding shortest paths in a weighted graph with positive or negative edge weights (but with no negative cycles). (wikipedia)
for k in range(V):
for i in range(V):
for j in range(V):
dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k]+ dist[k][j])
