Algorithm from leetcode
Reverse Nodes in k-Group (leecode-25)
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
node = next_head = ListNode(0)
node.next = head
start = end = head
while True:
cnt = 0
while end and cnt < k:
end = end.next
cnt += 1
if cnt == k:
prev, cur = end, start
for _ in range(k):
cur.next, prev, cur = prev, cur, cur.next
next_head.next = prev
next_head = start
start = end
else:
return node.next
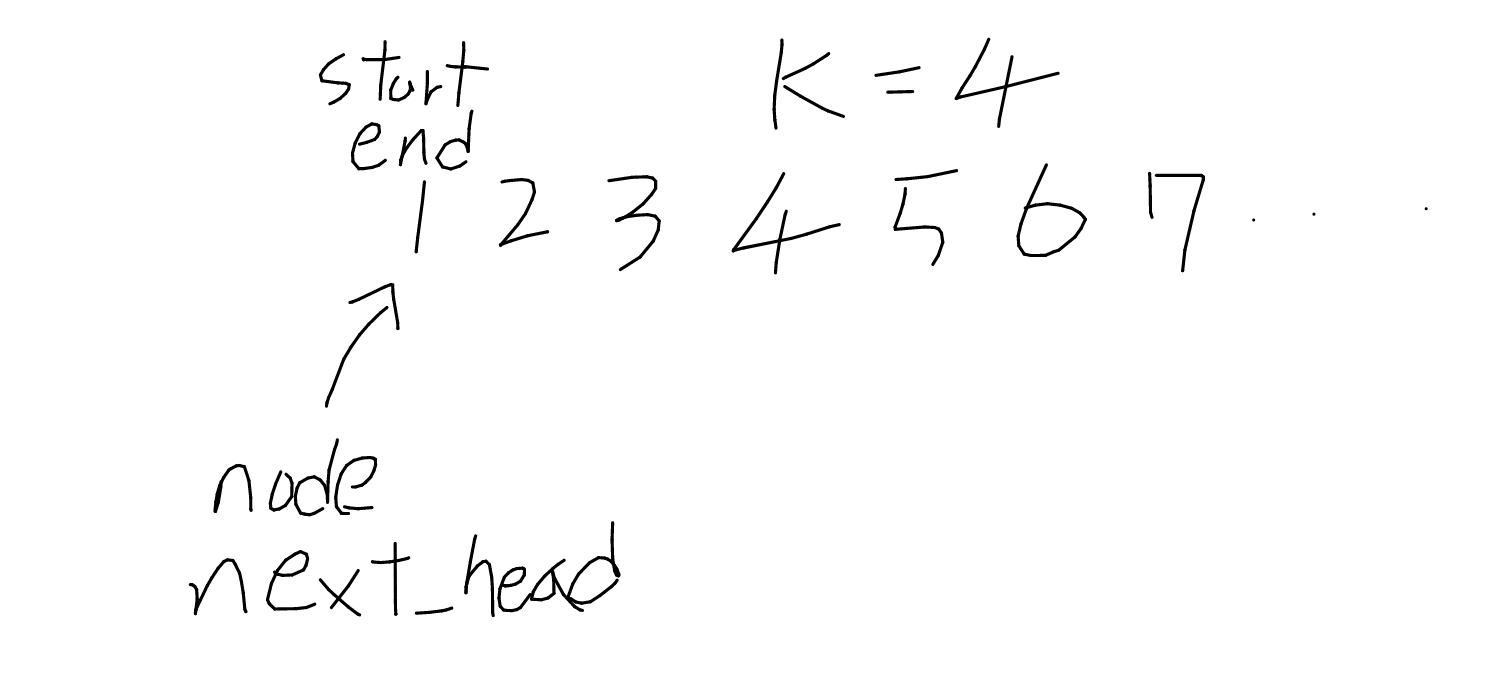
Iterate the ‘end’ Kth time. Reverse nodes from ‘start’ untill right before the ‘end’.
Combination Sum II (leecode-40)
Given a collection of candidate numbers (candidates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
if target == 0:
output.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(index, len(candidates)):
if target < candidates[i]:
return
if i > index and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]:
continue
path.append(candidates[i])
self.dfs(candidates, target-candidates[i], i+1, path, output)
path.pop()
Use dfs to find the paths. By writing ‘if target < candidates[i]:’ in for iterations, it takes less time.
Edit Distance (leetcode-72)
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
dp = [[0]*(a+1) for _ in range(b+1)]
for i in range(1,a+1):
dp[0][i] = i
for i in range(1,b+1):
dp[i][0] = i
for i in range(1,b+1):
for j in range(1,a+1):
if word1[j-1] == word2[i-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
else:
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j-1]) + 1
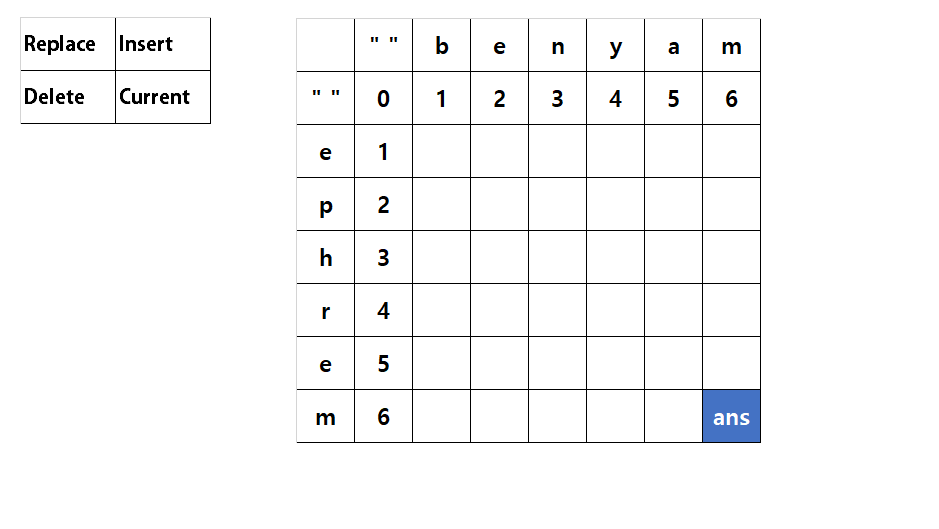
It is a key to find a sub problem.
Validate Binary Search Tree (leetcode-98)
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
if root.val <= left_child_val:
return False
left_child_val = root.val
root = root.right
If left_child val in inorder traversal is smaller than the root value, that is not BST.
Maximum Product Subarray (leetcode-152)
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which has the largest product.
prev_max, prev_min, max_value = nums[0], nums[0], nums[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
cur_max = max(nums[i]*prev_max, nums[i]*prev_min, nums[i])
cur_min = min(nums[i]*prev_max, nums[i]*prev_min, nums[i])
prev_max, prev_min = cur_max, cur_min
max_value = max(max_value, cur_max)
return max_value
Use Kadanes Algorithm with storing cur_max and cur_min.
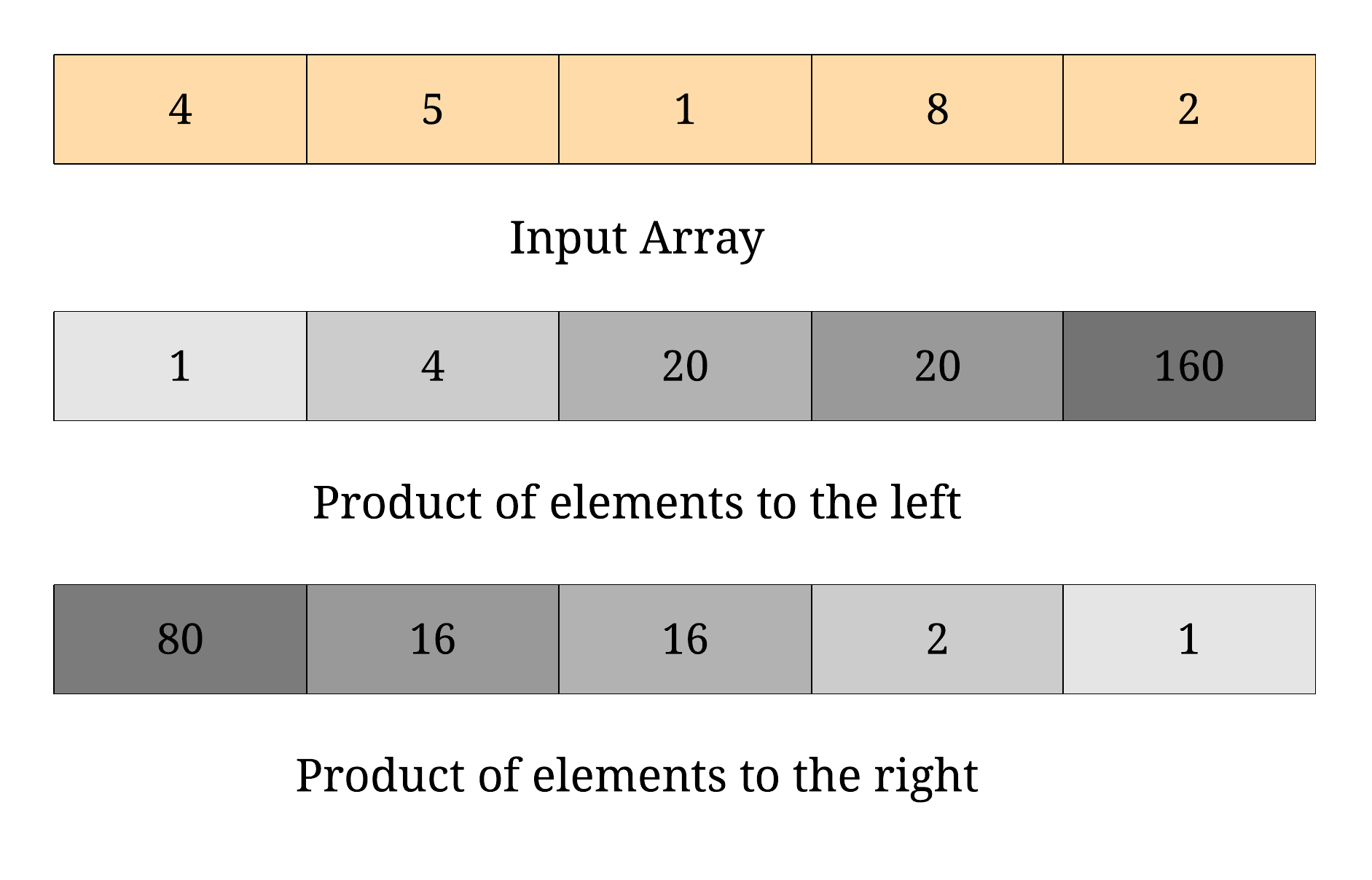
Product of Array Except Self (leetcode-238)
Given an array nums of n integers where n > 1, return an array output such that output[i] is equal to the product of all the elements of nums except nums[i].
storing left_prod and right_prod in array
for i in range(1,n):
left_prod[i] = nums[i-1] * left_prod[i-1]
for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):
right_prod[i] = nums[i+1] * right_prod[i+1]
for i in range(n):
output.append(left_prod[i]*right_prod[i])
wihtout storing left_prod and right_prod
for i in range(1,n):
output[i] = nums[i-1] * output[i-1]
for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):
output[i] = R * output[i]
R *= nums[i]
Calculate product of elements from left+1 to right-1 and Calculate product of elements from right-1 to left+1.
Multiply two arrays that are just calcaulated.
Trapping Rain Water (leetcode-42)
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.

brute Force
for i in range(1, len(height)):
left_max = 0
right_max = 0
left_max = max(height[:i])
right_max = max(height[i:len(height)])
min_building = min(left_max,right_max)
if min_building - height[i] < 0:
continue
ans += min_building - height[i]
storing left_prod and right_prod in array
for i in range(1,len(height)):
max_left[i] = max(max_left[i-1],height[i])
for i in range(len(height)-2,-1,-1):
max_right[i] = max(max_right[i+1],height[i])
for i in range(len(height)):
min_building = min(max_left[i], max_right[i])
ans += min_building - height[i]
two pointers
while i <= j:
max_left, max_right = max(max_left, height[i]), max(max_right, height[j])
if max_left <= max_right:
total_water += max_left - height[i]
i += 1
else:
total_water += max_right - height[j]
j -= 1
Subsets II (leetcode-90)
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
def dfs(self, nums, idx, path, output):
output.append(path[:])
for i in range(idx, len(nums)):
if i > idx and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
path.append(nums[i])
self.dfs(nums, i+1, path, output)
path.pop()
use dfs to append every elements but not duplicated one. if i > idx and nums[i] == nums[i-1] is the key.
Kth Largest Element in an Array (leetcode-215)
Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
heap = []
for i in nums:
if len(heap) < k:
heapq.heappush(heap, i)
elif i > heap[0]:
heapq.heapreplace(heap, i)
return heap[0]
Idea is to maintain a k size min-heap. Add k element to minheap, for next if element > minheap[0], then pop min and add the element
Merge k Sorted Lists (leetcode-23)
You are given an array of k linked-lists lists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order. Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list and return it.
merge sort
def merge(node1: ListNode, node2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = node = ListNode()
while node1 and node2:
if node1.val < node2.val:
node.next = node1
node1 = node1.next
else:
node.next = node2
node2 = node2.next
node = node.next
node.next = node1 if node1 else node2
return dummy.next
if not lists:
return
elif len(lists) == 1:
return lists[0]
mid = len(lists) // 2
left = merge_k_lists(lists[:mid])
right = merge_k_lists(lists[mid:])
return merge(left, right)
heap
heap = []
for node in lists:
while node:
heapq.heappush(heap, node.val)
node = node.next
dummy = node = ListNode()
while heap:
node.next = ListNode(heapq.heappop(heap))
node = node.next
return dummy.next
