Algorithm from leetcode(2)
Partition Equal Subset Sum(leetcode-416)
Given a non-empty array containing only positive integers, find if the array can be partitioned into two subsets such that the sum of elements in both subsets is equal.
bottom-up
# with only one number, we can form a subset only when the required sum is
# equal to its value
for j in range(1, s + 1):
dp[0][j] = nums[0] == j
# process all subsets for all sums
for i in range(1, numsLen):
for j in range(1, s + 1):
if dp[i - 1][j]: # if we can get the sum 'j' without the number at index 'i'
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]
elif j >= nums[i]: # else if we can find a subset to get the remaining sum
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]]
memoization+dfs
if remain in self.cache:
return self.cache[remain]
if remain == 0:
return True
if remain < 0 or i == len(self.nums):
return False
self.cache[remain] = self.dfs(remain - self.nums[i], i + 1) or self.dfs(remain, i + 1)
return self.cache[remain]
Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array(leetcode-34)
Given an array of integers nums sorted in ascending order, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
def search(nums, target):
n = len(nums)
position = n
left,right = 0, n-1
while left <= right:
mid = (left+right) // 2
if nums[mid] >= target:
position = mid
right = mid-1
else:
left = mid+1
return position
It is a key to think first positions of target and target+1.
For example, suppose there are nums like 3 3 3 5 5 5 6 7 8 and target is 5.
First, find the first position of ‘5’ and then find the first position of ‘6’. first position of ‘6’ - 1 will be the last position of ‘5’.
Minimum Height Trees (leetcode-310)
while n > 2:
n -= len(leaves)
new_leaves = set()
for leave in leaves:
neighbor = graph[leave].pop()
graph[neighbor].remove(leave)
if len(graph[neighbor]) == 1:
new_leaves.add(neighbor)
It is a key to remove every leaves from the graph until 2 nodes left.
Best Time To Buy and Sell Stock (leetcode-121)
If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock), design an algorithm to find the maximum profit.
for n in prices:
if n < min_:
min_ = n
else:
max_ = max(max_,n-min_)
Split Array Largest Sum (leetcode-410)
Given an array nums which consists of non-negative integers and an integer m, you can split the array into m non-empty continuous subarrays.
def cnt_p(value):
cnt, cur = 0, nums[0]
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
if cur + nums[i] > value:
cur = nums[i]
cnt += 1
else:
cur += nums[i]
return cnt
It is a key to use Binary Search. The search range will be from maximum of the nums’s array to sum of the nums’s array.
Longest Mountain in Array
Given an array A of integers, return the length of the longest mountain.
left, right
n = len(A)
a = [0]*n
b = [0]*n
for i in range(n-1):
if A[i] < A[i+1]:
a[i+1] = a[i]+1
for i in range(n-1,0,-1):
if A[i] < A[i-1]:
b[i-1] = b[i]+1
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
if a[i] != 0 and b[i] != 0:
ans = max(ans,a[i]+b[i])
return ans+1
###
n = len(A)
up,down,ans = 0,0,0
for i in range(1,n):
if A[i-1] == A[i] or (down > 0 and A[i-1] < A[i]):
up = down = 0
if A[i-1] < A[i]:
up += 1
if A[i-1] > A[i]:
down += 1
if up and down:
ans = max(ans, up + down + 1)
return ans
###
n = len(A)
l,r,ans = 0,0,0
for i in range(1,n-1):
if A[i-1] < A[i] > A[i+1]:
l = r = i
while l > 0 and A[l-1] < A[l]:
l -= 1
while r < n-1 and A[r+1] < A[r]:
r += 1
ans = max(ans, r-l+1)
return ans
Pseudo-Palindromic Paths in a Binary Tree (leetcode-1457)
Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be pseudo-palindromic if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
def dfs(node, seen):
nonlocal ans
seen ^= (1 << node.val)
if node.left:
dfs(node.left, seen)
if node.right:
dfs(node.right, seen)
if not node.left and not node.right:
if seen & (seen-1) == 0:
ans += 1
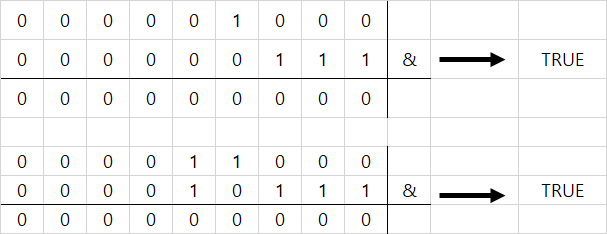
It is a key to use bitmask in order to use less space complexity.
